Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms & Modern Treatment Options
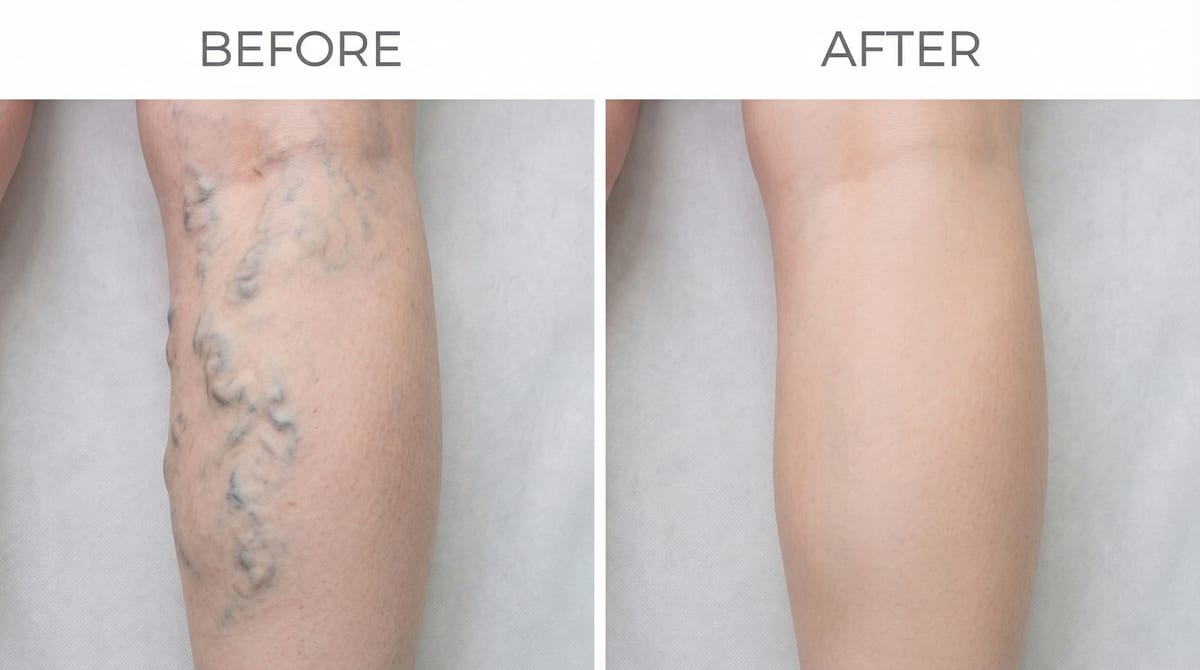
Varicose veins are one of the most common vascular conditions, affecting up to 30% of adults at some point in their lives. These enlarged, twisted veins most often appear in the legs and can range from a minor cosmetic concern to a source of significant discomfort and, in some cases, serious medical complications. Understanding the causes, recognising the symptoms, and knowing about the modern treatment options available can help you take control of your vascular health.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Veins carry blood back to the heart, and those in the legs must work against gravity to do so. Inside these veins are tiny one-way valves that open to allow blood to flow upward and close to prevent it from flowing backward. When these valves become weakened or damaged, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to stretch, swell, and become visibly twisted beneath the skin. This condition is known as venous insufficiency, and the resulting enlarged veins are called varicose veins.
While spider veins (smaller, flat, red or purple veins close to the skin surface) are generally a cosmetic issue, varicose veins are larger, deeper, and more likely to cause symptoms that affect your daily quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins. Understanding these can help you assess your own risk and take preventive steps where possible.
Genetics
Family history is one of the strongest predictors of varicose veins. If one or both of your parents had varicose veins, your risk of developing them is significantly higher. Inherited factors can affect the strength of vein walls and the function of venous valves.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Occupations that require long hours of standing or sitting in one position place extra pressure on the veins of the legs. Teachers, nurses, hairdressers, retail workers, and office professionals are at particular risk. When you stay in one position for extended periods, blood does not flow as efficiently, increasing the strain on venous valves.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the volume of blood in the body increases to support the developing baby, placing additional pressure on the veins. Hormonal changes also cause vein walls to relax, and the growing uterus can compress pelvic veins. Varicose veins that develop during pregnancy often improve within a few months after delivery, but they may worsen with subsequent pregnancies.
Age
As we age, the valves in our veins naturally wear down, and vein walls lose elasticity. This gradual deterioration means that varicose veins become more common with advancing age, though they can develop at any stage of life.
Other Risk Factors
Additional factors include obesity, which increases pressure on leg veins; a history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT); and being female, as hormonal fluctuations during menstruation and menopause can relax vein walls.
Recognising the Symptoms
Varicose veins can present with a wide range of symptoms, and not everyone with visible veins will experience discomfort. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Visible, bulging veins — dark purple or blue veins that appear twisted and rope-like, usually on the calves or inner thighs
- Aching and throbbing — a dull, heavy ache in the legs, especially after prolonged standing or towards the end of the day
- Heaviness and fatigue — a feeling of tiredness and weight in the legs that may worsen with activity
- Swelling — particularly around the ankles and lower legs, often more noticeable in the evening
- Itching and burning — skin irritation around the affected veins
- Skin changes — in advanced cases, the skin around varicose veins may become discoloured (brown or reddish), thickened, or develop eczema-like changes
- Leg cramps — especially at night, with a restless feeling in the legs
If left untreated, chronic venous insufficiency can lead to more serious complications including venous ulcers (non-healing wounds near the ankle), spontaneous bleeding from surface veins, and superficial thrombophlebitis (inflammation and clotting in a surface vein).
Modern Treatment Options
The treatment of varicose veins has advanced dramatically in recent years. Traditional vein stripping surgery, which involved general anaesthesia and lengthy recovery, has largely been replaced by minimally invasive techniques that are performed as outpatient procedures with rapid recovery times.
Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
Endovenous laser ablation uses targeted laser energy delivered through a thin fibre inserted into the affected vein under ultrasound guidance. The laser heats the vein wall, causing it to seal shut. Blood then naturally reroutes through healthy veins. The procedure is performed under local anaesthesia, takes about 30 to 45 minutes, and most patients return to normal activities within a day or two.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
Similar to laser ablation, radiofrequency ablation uses radiofrequency energy to heat and close the damaged vein. A catheter is inserted into the vein, and controlled thermal energy is delivered along its length. RFA is known for causing less post-procedure discomfort than laser treatment and has excellent long-term success rates exceeding 95%.
VenaSeal (Medical Adhesive)
VenaSeal is one of the newest treatments available. It uses a medical-grade adhesive (cyanoacrylate) to permanently seal the diseased vein. The adhesive is delivered through a small catheter, and the vein is closed almost immediately. One of the key advantages of VenaSeal is that it does not require tumescent anaesthesia (the multiple small injections along the vein that are needed for laser and radiofrequency treatments), making it a particularly comfortable option for patients.
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a chemical solution (sclerosant) directly into the varicose or spider veins. The solution irritates the vein lining, causing it to collapse and eventually be absorbed by the body. Foam sclerotherapy, where the solution is mixed with air to create a foam, is particularly effective for larger veins and is often used in combination with other treatments for comprehensive results.
When Should You Seek Treatment?
You should consider seeing a vascular surgeon if you experience any of the following:
- Your varicose veins cause persistent pain, heaviness, or swelling
- You notice skin changes such as discolouration, hardening, or eczema around the veins
- A varicose vein has bled, even if the bleeding stopped on its own
- You develop a sore or ulcer near the ankle that is slow to heal
- One leg becomes suddenly swollen, red, and painful (which may indicate a blood clot)
- Your symptoms are affecting your quality of life, sleep, or ability to work
Early assessment is important because varicose veins tend to worsen over time. What begins as a mild cosmetic concern can progress to chronic symptoms and complications if the underlying venous insufficiency is not addressed.
Prevention Tips
While you cannot change your genetics, there are practical steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing varicose veins or slow the progression of existing ones:
- Stay active — regular walking, swimming, or cycling strengthens the calf muscle pump, which helps push blood back toward the heart
- Maintain a healthy weight — excess weight increases pressure on leg veins
- Elevate your legs — when resting, raise your legs above heart level for 15 to 20 minutes several times a day
- Avoid prolonged standing or sitting — take regular breaks to walk around and flex your calves
- Wear compression stockings — medical-grade compression stockings support the veins and improve blood flow, especially if you are on your feet for long periods
- Stay hydrated — good hydration supports healthy blood flow and helps prevent blood from thickening
Varicose veins are a treatable condition, and modern procedures offer excellent results with minimal downtime. If you are concerned about varicose veins, Dr. Medani can provide a thorough assessment using duplex ultrasound and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.